lens thickness is surfaced to which measurement|high index lens thickness chart : exporting Box Measurement Definitions and Additional Verbiage to help with following formulas. A = Width of the Lens. B = Height of the Lens. ED = Effective Diameter (longest diameter of lens) DBL = . WEBCannonball Bay Online Slot. (5 Reels, 25 Paylines) Cannonball Bay puts you in the middle of a Caribbean pirate treasure hunt. While sailing the azure waters of the .
{plog:ftitle_list}
William and Sly. A cozy open-world 3D adventure based on the popular 'William and Sly' Flash games. Explore a wild mountain landscape as a fox in search of mushrooms and .
To measure center thickness, use an external caliper, a caliper with protruding pinchers. To measure edge thickness, a clamping-style caliper will work best. Clamp the caliper onto the thickest location until the pinchers or .
The calculator uses a proprietary formula that combines the refractive index of the lens material, the lens prescription, and the frame dimensions to calculate lens thickness. This includes the thinnest point .Box Measurement Definitions and Additional Verbiage to help with following formulas. A = Width of the Lens. B = Height of the Lens. ED = Effective Diameter (longest diameter of lens) DBL = .The center thickness of an optical component, most notably a lens, is the material thickness of the component measured at the center. Center thickness is measured across the mechanical axis of the lens, defined as the axis .Using a simple job as a sample, let’s review the impact of center thickness, material index of refraction and decentration on lens edge thickness. We’ll look at center thickness followed by the material index of refraction and finally the .
Learn more about refractive index and lens thickness. Lens thickness will depend on the strength of your prescription, your pupillary distance (PD), the size of the frame, and the lens material.This article offers ways to assess the factors that affect lens thickness and can help you determine whether thin, thinner or thinnest lenses will result in the best outcome for your patient. Define what a ‘thick lens’ is, and calculate how to measure thickness. Understand the relationship between thickness, curvature of the surfaces, refractive index and how these contribute to the power of the lens. .
what thickness lens for 4.75
Knowing the advantages and disadvantages of each lens type is crucial when choosing between optics as each has its own purpose. Understanding optical lens geometries helps anyone, . Non-contact measurements have the advantages of high accuracy, stability and operational flexibility, and are therefore widely used in modern industrial measurements [8].The chromatic confocal system, as a non-contact technique, is gradually playing a more important role in the field of thickness measurement of lens centres due to its fast response time and . The correlation between lens thickness and age and ocular biometric factors. Scatter plots showing the correlation between lens thickness and age (a), central corneal thickness (b), anterior chamber depth (c), white . Correlations of actual lens position with age, mean K data, AL, ACD, anterior segment depth, lens thickness, CD distance, and refraction. ACD anterior chamber depth, AL axial length, ALP actual lens position, ASD .
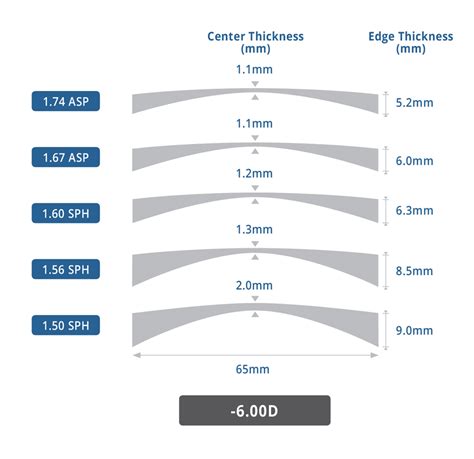
Let’s take a look and give you a better idea. Starting with 1.61 vs 1.67 high index lenses — the 1.67 lens is extremely thin whereas despite still being stylish, the 1.61 lens is extra-thin. The 1.67 lens is a great choice for extra-strong prescriptions. What about 1.67 vs 1.74 high index lenses?
Due to the negative diopter lens constructions of conventional remote sensing catadioptric telescopes, the corrector lens produces divergent optical property, resulting in difficulties of measuring the center thickness of the lenses and the air gaps between lens interfaces. One solution to address this issue is to incorporate a positive diopter lens on the .White light interferometry (WLI) is a common system of measurement with a long history and a variety of applications, which currently include surface profiling 1, medical imaging, and — as in the past — thickness measurement.Also known as coherence scanning interferometry (CSI), vertical scanning interferometry (VSI), and optical coherence tomography (OCT), these . If you do not have this information, then lens thickness can be measured directly using an external or clamping-style caliper, depending on the type of lens. Both calipers work by clamping onto a lens and providing the measurement via a dial or measurement scale. When you measure lens thickness, only the thickest part should be measured. The key to solve the high precision component parameters measurement is getting exact locations of the vertex and the centre of the sphere of the components surfaces, which is the common problem .
Dimensional tolerances for lenses . Diameter tolerance of 25 ± 0.1 mm means that the lens must have diameter between 24.9 and 25.1 mm . Lens thickness is almost always defined as the center thickness . Typical tolerances for small (10 - 50 mm) optics: Diameter +0/-0.1 mm . Thickness ± 0.2 mm . Clear aperture is defined as the area of the surface After being collimated by the lens and split by the beam splitter BS, a He-Ne laser beam is split into two interference beams. . Surface and thickness measurement of a transparent film using wavelength scanning interferometry.[J] Opt Express, 20 (19) (2012), pp. 21450-21456. View in Scopus Google Scholar [34] D.S. Kim, Y.J. Cho.Center Thickness – The distance from a primary principal plane location to the end of an element. $\small{\text{ET}}$ Edge Thickness – A calculated value that depends on radii, diameter, and center thickness of a lens. $ \small{d_b} $ Entrance Beam Diameter – Diameter of collimated light entering an axicon. $ \small{d_r} $
To measure the thickness (d) of a thin film, the complex refractive indices and incident angles should be known in advance.The total reflectance at each wavelength according to d can be calculated using such information. As a result, the thin-film thickness d can be determined as a specific value which makes the modeled total reflectance spectrum most . Centre and Edge Thickness. The measurement of centre thickness provides key information on the rigidity of a lens and is also used to calculate oxygen transmissibility. Central, peripheral and edge thickness can be measured using dial or digital gauges ( Fig. 14.2). The gauges should have a readout resolution of 1 µm and a specified accuracy . A noncontact, fast and precise optical measuring setup based upon a confocal chromatic probe, which can be used to measure central lens thickness ranging from 30 μm up to 25 mm, is presented.
A new confocal measurement for lens refractive index and thickness is proposed based on the property that the peak of an axial intensity curve precisely corresponds to the focus of the objective .These measurements tell us how far away the OC of the lens is from the center of the frames. It is important to know this because the thickness of a lens is greatly affected by the amount of decentration. DEC = FRAME PD - PATIENT PD. Vert DEC = OC HT - (B/2)
Because measurement of thickness of soft lenses entails additional problems, attempts at measurement, such as those of Pearson (1980), have been confined to the geometric centre, In the case of hard lenses, it would appear that for decades both . The healthy central cornea is aspheric and prolate (the central curvature is steeper than the periphery).[1] Attempts to measure the cornea were made as early as the 1600s by Scheiner, who compared reflections produced by glass spheres whose diameters were known to the reflections from the anterior surface of the cornea.[2] The central keratometric values vary . A new method for lens thickness and air gap measurement is proposed. • The measurement method based on the frequency-shifted confocal feedback. • The measurement system has high sensitivity and belong to the heterodyne modulation. • The uncertainty is better than 0.0005 mm and the accuracy reaches micron range.
It was noted that the confocal measurement has a minimum measurable thickness due to the axial resolution. In [12], a novel differential confocal system was used to measure the lens thickness with improved measurement accuracy by Wang et al. Furthermore, the confocal reflection methods can measure the refractive index of the transparent material.
In optics production, the high quality of the single lens is the prerequisite for high-precision optical systems. With the OptiSurf ® LTM (Lens Thickness Measurement), TRIOPTICS offers a precise center thickness measurement system for single lenses and doublets that seamlessly integrates into any production process. The high precision low-coherence interferometry is .The chromatic confocal technology (CCT) has ultra-high distance measurement resolution and the characteristics of multi-surface tomography. Based on the principle of optical dispersion and confocal, the technology achieves accurate axial position or micro-displacement measurement. The radial gradient index (GRIN) lens is a typical important inhomogeneous material. Its . Other notable measurements include lens thickness, white-to-white distance, estimated lens position, and corneal thickness. However, these measurements play less of a critical role for calculations. White-to-white measurements become particularly important when an anterior chamber IOL (ACIOL) or an implantable collamer lens (ICL) will be . [7][8][9] Therefore, the measurement of GRIN lens thickness parameters requires more and more precision. In recent years, scholars have proposed the use of color confocal method, 10 laser .
The OptiSurf LTM from TRIOPTICS enables contactless and highly accurate center thickness and sagittal height measurement of single lenses and doublets. . OptiSurf® LTM-Increases Production Efficiency at Pfeiffer Präzisionsoptik TRIOPTICS‘ Solution for Non-contact Lens Center Thickness Measurement Significantly Reduces Reject Volume .Lens thickness will depend on the strength of your prescription, your pupillary distance (PD), the size of the frame, and the lens material.. Refractive index. Lens materials are classified on their refractive index.This refractive index is the ratio of the speed of light when it travels through air to the speed of light when it passes through the lens material.
recommended lens thickness for glasses
optical lens thickness chart
Single Point Heat Sealer Tester importer
Resultado da Help us with translations
lens thickness is surfaced to which measurement|high index lens thickness chart